Tag: grammar
Uses of Also, Too and So The word also goes before the main verb and after the verb to be. The word too goes at the end of the …
Parts of speech table This is summary of the 8 parts of speech. This pats; Verb, Noun, Adjective, Adverb, Pronoun, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection. Follow the list for function, job, …
Nouns that can be Countable and Uncountable Sometimes, the same noun can be countable and uncountable, often with a change of meaning. Examples; hair, light, noise, paper, room, time, …
Differences Between “Which” and “That” Use ‘which’ with a comma for non-restrictive relative clauses. Non-restrictive relative clauses give additional, but not essential information. Use ‘that’ without comma for restrictive …
Common Grammar Mistakes – English Study The verb be, Prepositions, auxiliary verbs, 3rd person’s, past tense, word order, comparatives, adverbs; follow the examples;
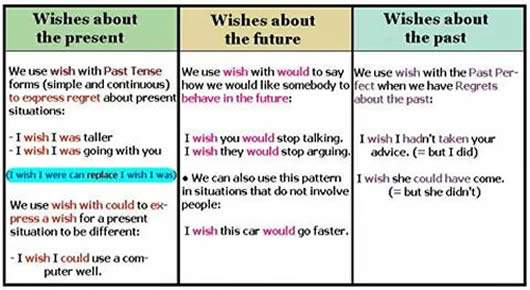
Uses of Wishes With Tenses Wishes about the present, Wishes about the future, Wishes about the past. We use wish with Past Tense forms(simple and continuous) to express regret …
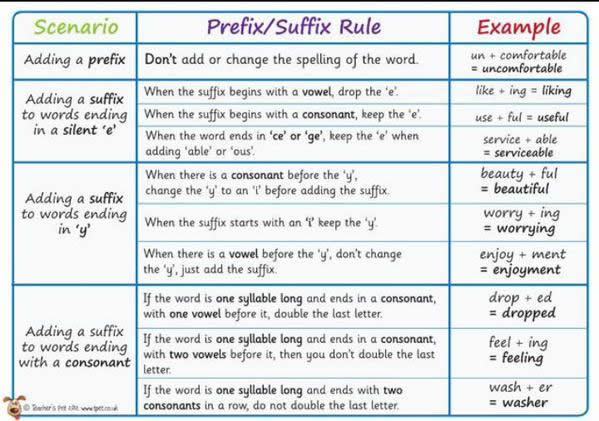
Rules for Prefixes and Suffixes Adding a prefix, Adding a suffix to words ending in a silent ‘e’, adding a suffix to words ending in ‘y’, adding a suffix …
Uses of Either and Neither With Examples Either A or B / Neither A nor B / Either (one) of (A&B) / Neither (one) of (A&B) . Follow the …
How to Ask Questions in English Uses of who, where, what, when, why, which, how, how many, how much, how long, how far, how often. Follow the list (example …
Uses of Must and Differences Between Must and Have to Uses of Must; obligation, deduction, emphasize necessity, strong recommendation, musn’t=prohibition. For example sentences follow the list;